Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: June 2023
- Journal: Computer Graphics Forum
- Volume: 42
- Open Access: yes
- Number: 3
- Location: Leipzig, Germany
- Lecturer: Johannes Eschner
- ISSN: 1467-8659
- Event: EuroVis 2023
- DOI: 10.1111/cgf.14836
- Pages: 12
- Publisher: WILEY
- Pages: 361 – 372
- Keywords: Empirical studies in visualization, Animation
Abstract
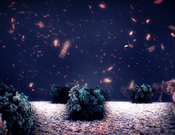
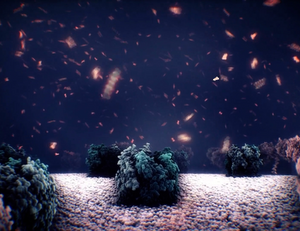
3D animations are an effective method to learn about complex dynamic phenomena, such as mesoscale biological processes. The animators’ goals are to convey a sense of the scene’s overall complexity while, at the same time, visually guiding the user through a story of subsequent events embedded in the chaotic environment. Animators use a variety of visual emphasis techniques to guide the observers’ attention through the story, such as highlighting, halos – or by manipulating motion parameters of the scene. In this paper, we investigate the effect of smoothing the motion of contextual scene elements to attract attention to focus elements of the story exhibiting high-frequency motion. We conducted a crowdsourced study with 108 participants observing short animations with two illustrative motion smoothing strategies: geometric smoothing through noise reduction of contextual motion trajectories and visual smoothing through motion blur of context items. We investigated the observers’ ability to follow the story as well as the effect of the techniques on speed perception in a molecular scene. Our results show that moderate motion blur significantly improves users’ ability to follow the story. Geometric motion smoothing is less effective but increases the visual appeal of the animation. However, both techniques also slow down the perceived speed of the animation. We discuss the implications of these results and derive design guidelines for animators of complex dynamic visualizations.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{eschner-2023-ims,
title = "Illustrative Motion Smoothing for Attention Guidance in
Dynamic Visualizations",
author = "Johannes Eschner and Peter Mindek and Manuela Waldner",
year = "2023",
abstract = "3D animations are an effective method to learn about complex
dynamic phenomena, such as mesoscale biological processes.
The animators’ goals are to convey a sense of the
scene’s overall complexity while, at the same time,
visually guiding the user through a story of subsequent
events embedded in the chaotic environment. Animators use a
variety of visual emphasis techniques to guide the
observers’ attention through the story, such as
highlighting, halos – or by manipulating motion parameters
of the scene. In this paper, we investigate the effect of
smoothing the motion of contextual scene elements to attract
attention to focus elements of the story exhibiting
high-frequency motion. We conducted a crowdsourced study
with 108 participants observing short animations with two
illustrative motion smoothing strategies: geometric
smoothing through noise reduction of contextual motion
trajectories and visual smoothing through motion blur of
context items. We investigated the observers’ ability to
follow the story as well as the effect of the techniques on
speed perception in a molecular scene. Our results show that
moderate motion blur significantly improves users’ ability
to follow the story. Geometric motion smoothing is less
effective but increases the visual appeal of the animation.
However, both techniques also slow down the perceived speed
of the animation. We discuss the implications of these
results and derive design guidelines for animators of
complex dynamic visualizations.",
month = jun,
journal = "Computer Graphics Forum",
volume = "42",
number = "3",
issn = "1467-8659",
doi = "10.1111/cgf.14836",
pages = "12",
publisher = "WILEY",
pages = "361--372",
keywords = "Empirical studies in visualization, Animation",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2023/eschner-2023-ims/",
}

 paper
paper video
video