Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: June 2023
- Journal: Computer Graphics Forum
- Volume: 42
- Open Access: yes
- Number: 8
- Location: Delft
- Lecturer: Markus Schütz
- Article Number: e14877
- ISSN: 1467-8659
- Event: High Performance Graphics
- DOI: 10.1111/cgf.14877
- Pages: 12
- Publisher: WILEY
- Conference date: 2023
- Pages: 1 – 12
- Keywords: point cloud rendering, level of detail, LOD
Abstract
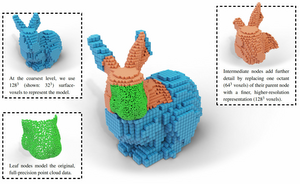
About: We introduce a GPU-accelerated LOD construction process that creates a hybrid voxel-point-based variation of the widely used layered point cloud (LPC) structure for LOD rendering and streaming. The massive performance improvements provided by the GPU allow us to improve the quality of lower LODs via color filtering while still increasing construction speed compared to the non-filtered, CPU-based state of the art.Background: LOD structures are required to render hundreds of millions to trillions of points, but constructing them takes time.
Results: LOD structures suitable for rendering and streaming are constructed at rates of about 1 billion points per second (with color filtering) to 4 billion points per second (sample-picking/random sampling, state of the art) on an RTX 3090 -- an improvement of a factor of 80 to 400 times over the CPU-based state of the art (12 million points per second). Due to being in-core, model sizes are limited to about 500 million points per 24GB memory.
Discussion: Our method currently focuses on maximizing in-core construction speed on the GPU. Issues such as out-of-core construction of arbitrarily large data sets are not addressed, but we expect it to be suitable as a component of bottom-up out-of-core LOD construction schemes.
Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{SCHUETZ-2023-LOD,
title = "GPU‐Accelerated LOD Generation for Point Clouds",
author = "Markus Sch\"{u}tz and Bernhard Kerbl and Philip Klaus and
Michael Wimmer",
year = "2023",
abstract = "About: We introduce a GPU-accelerated LOD construction
process that creates a hybrid voxel-point-based variation of
the widely used layered point cloud (LPC) structure for LOD
rendering and streaming. The massive performance
improvements provided by the GPU allow us to improve the
quality of lower LODs via color filtering while still
increasing construction speed compared to the non-filtered,
CPU-based state of the art. Background: LOD structures
are required to render hundreds of millions to trillions of
points, but constructing them takes time. Results: LOD
structures suitable for rendering and streaming are
constructed at rates of about 1 billion points per second
(with color filtering) to 4 billion points per second
(sample-picking/random sampling, state of the art) on an RTX
3090 -- an improvement of a factor of 80 to 400 times over
the CPU-based state of the art (12 million points per
second). Due to being in-core, model sizes are limited to
about 500 million points per 24GB memory. Discussion: Our
method currently focuses on maximizing in-core construction
speed on the GPU. Issues such as out-of-core construction of
arbitrarily large data sets are not addressed, but we expect
it to be suitable as a component of bottom-up out-of-core
LOD construction schemes.",
month = jun,
journal = "Computer Graphics Forum",
volume = "42",
number = "8",
articleno = "e14877",
issn = "1467-8659",
doi = "10.1111/cgf.14877",
pages = "12",
publisher = "WILEY",
pages = "1--12",
keywords = "point cloud rendering, level of detail, LOD",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2023/SCHUETZ-2023-LOD/",
}