Information
- Publication Type: Bachelor Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: 2016
- Date (Start): April 2015
- Date (End): August 2016
- Matrikelnummer: 0726342
- Note: 1
- First Supervisor: Ivan Viola
Abstract
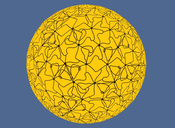
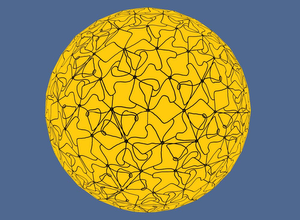
Visualizing cells, in particular cell membranes, is the inspiration for this work. The goal of the presented methods is the efficient visualization of phospholipid membranes. A prominent role hereby plays the concept of seamlessly texturing a surface in threedimensional space. By using suitable texture patches, memory consumption can be kept low. The developed algorithm first creates a texture mesh that stays faithful to the surface structure of a user-provided input-mesh. This texture mesh consists of equilateral triangles. The triangulation is achieved by first simulating repulsion between the vertices making up the texture mesh. This way they are moved around on the surface of the input-mesh until they are uniformly distributed. Mapping texture onto equilateral triangles becomes trivial if triangular texture patches are assumed as well. Thus, seamless texturing is achieved. The implementation is described in detail, followed by the demonstration of results. Also, an exemplary performance-analysis is given, highlighting benefits and shortcomings of the algorithm, especially concerning runtime. Additionally, a short overview of related and prior work is given. The used framework is Unity 3D.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@bachelorsthesis{glinzner-2016-tex,
title = "Texturing of 3D Objects using Simple Physics and Equilateral
Triangle Patches",
author = "Matthias Glinzner",
year = "2016",
abstract = "Visualizing cells, in particular cell membranes, is the
inspiration for this work. The goal of the presented methods
is the efficient visualization of phospholipid membranes. A
prominent role hereby plays the concept of seamlessly
texturing a surface in threedimensional space. By using
suitable texture patches, memory consumption can be kept
low. The developed algorithm first creates a texture mesh
that stays faithful to the surface structure of a
user-provided input-mesh. This texture mesh consists of
equilateral triangles. The triangulation is achieved by
first simulating repulsion between the vertices making up
the texture mesh. This way they are moved around on the
surface of the input-mesh until they are uniformly
distributed. Mapping texture onto equilateral triangles
becomes trivial if triangular texture patches are assumed as
well. Thus, seamless texturing is achieved. The
implementation is described in detail, followed by the
demonstration of results. Also, an exemplary
performance-analysis is given, highlighting benefits and
shortcomings of the algorithm, especially concerning
runtime. Additionally, a short overview of related and prior
work is given. The used framework is Unity 3D.",
note = "1",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2016/glinzner-2016-tex/",
}
 paper
paper