Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: January 2013
- TU Wien Library:
- First Supervisor:
Abstract
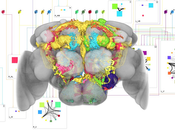
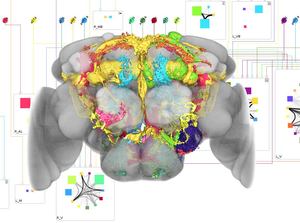
Neuroscientists study the function of neural circuits in the brain of the common fruit fly Drosophila Melanogaster to discover how complex behavior is generated. Through a combination of molecular-genetic techniques and confocal microscopy the scientists are able to highlight single neurons and produce three-dimensional images of the fly’s brain. Neurons are segmented, annotated, and compiled into a digital atlas. Brain atlases offer tools for exploring and analyzing their underlying data. To establish models of neural information processing, knowledge about possible connections between individual neurons is necessary. Connections can occur when arborizations (the terminal branchings of nerve fibers) of two neurons are overlapping. However, analyzing overlapping objects using traditional volumetric visualization is difficult since the examined objects occlude each other. A more abstract form of representation is therefore required. The work in this thesis was motivated by a manually constructed two-dimensional circuit diagram of potential neuronal connections that represents a novel way of visualizing neural connectivity data. Through abstracting the complex volumetric data, the diagram offers an intuitive and clear overview of potential connectivity. In collaboration with a group of neuroscientists neuroMap was designed and implemented in an attempt to deliver the visual features and encoded information of this circuit diagram in an automatically generated interactive graph, with the goal of facilitating hypothesis formation and exploration of neural connectivity. In this thesis the visual and interaction design decisions that went into neuroMap are presented, as well as the result of evaluative discussions that shows that the integration of this novel type of visualization into the existing datamining infrastructure of our clients is indeed beneficial to their research.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@mastersthesis{Sorger_2013_nMI,
title = "neuroMap - Interactive Graph-Visualization of the Fruit
Fly’s Neural Circuit",
author = "Johannes Sorger",
year = "2013",
abstract = "Neuroscientists study the function of neural circuits in the
brain of the common fruit fly Drosophila Melanogaster to
discover how complex behavior is generated. Through a
combination of molecular-genetic techniques and confocal
microscopy the scientists are able to highlight single
neurons and produce three-dimensional images of the fly’s
brain. Neurons are segmented, annotated, and compiled into a
digital atlas. Brain atlases offer tools for exploring and
analyzing their underlying data. To establish models of
neural information processing, knowledge about possible
connections between individual neurons is necessary.
Connections can occur when arborizations (the terminal
branchings of nerve fibers) of two neurons are overlapping.
However, analyzing overlapping objects using traditional
volumetric visualization is difficult since the examined
objects occlude each other. A more abstract form of
representation is therefore required. The work in this
thesis was motivated by a manually constructed
two-dimensional circuit diagram of potential neuronal
connections that represents a novel way of visualizing
neural connectivity data. Through abstracting the complex
volumetric data, the diagram offers an intuitive and clear
overview of potential connectivity. In collaboration with a
group of neuroscientists neuroMap was designed and
implemented in an attempt to deliver the visual features and
encoded information of this circuit diagram in an
automatically generated interactive graph, with the goal of
facilitating hypothesis formation and exploration of neural
connectivity. In this thesis the visual and interaction
design decisions that went into neuroMap are presented, as
well as the result of evaluative discussions that shows that
the integration of this novel type of visualization into the
existing datamining infrastructure of our clients is indeed
beneficial to their research.",
month = jan,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2013/Sorger_2013_nMI/",
}
 Poster
Poster Thesis
Thesis