Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: December 2009
- Date (Start): 2009
- Date (End): 2009
- TU Wien Library:
- Diploma Examination: 16. December 2009
- First Supervisor:
Abstract
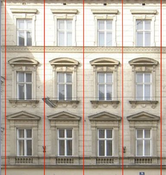
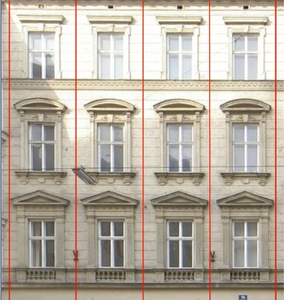
Building facades typically consist of multiple similar tiles which are arranged quite strictly in grid-like structures. The proposed method takes advantage of translational symmetries and is able to analyze and segment facades into tiles assuming that there are horizontal and vertical repetitions of similar tiles. In order to solve this quite complex computer vision task efficiently a Monte Carlo approach is presented which samples only selected image features. This method, which is meant to be a preprocessing step for more sophisticated tile segmentation and window identification in urban reconstruction tasks, is able to robustly identify orthogonal repetitive patterns on rectified facade images even if they are partially occluded, shadowed, blurry or otherwise damaged. Additionally, the algorithm is very running time efficient because neither quality of results nor the computational complexity are significantly depending on the image size.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@mastersthesis{recheis-2009-arr,
title = "Automatic Recognition of Repeating Patterns in Rectified
Facade Images",
author = "Meinrad Recheis",
year = "2009",
abstract = "Building facades typically consist of multiple similar tiles
which are arranged quite strictly in grid-like structures.
The proposed method takes advantage of translational
symmetries and is able to analyze and segment facades into
tiles assuming that there are horizontal and vertical
repetitions of similar tiles. In order to solve this quite
complex computer vision task efficiently a Monte Carlo
approach is presented which samples only selected image
features. This method, which is meant to be a preprocessing
step for more sophisticated tile segmentation and window
identification in urban reconstruction tasks, is able to
robustly identify orthogonal repetitive patterns on
rectified facade images even if they are partially occluded,
shadowed, blurry or otherwise damaged. Additionally, the
algorithm is very running time efficient because neither
quality of results nor the computational complexity are
significantly depending on the image size.",
month = dec,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2009/recheis-2009-arr/",
}
 figure
figure thesis
thesis