Abstract
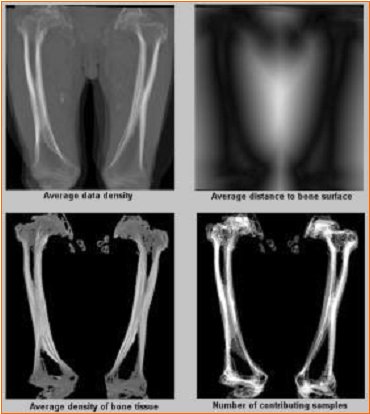
Automatic segmentation of bony structures in CT angiography datasets is an essential pre-processing step necessary for most visualization and analysis tasks. Since traditional density and gradient operators fail in non-trivial cases (or at least requiere extensive operator work), we propose a new method for segmentation of CTA data based on a probabilistic atlas. Storing densities and marks of previously manually segmented tissues to the atlas can constitute a statistical information base for latter accurate segmentation. In order to eliminate dimensional and anatomic variability of the atlas input datasets, these have to be spatially normalized (registered) first by applying a non-rigid transformation. After this trasnformation, densities and tissue masks are statistically processed (e.g averaged) within the atlas. Records in the atlas can be later evaluated for estimating the probability of bone tissue in a voxel of an unsegmented dataset.Keywords:CT Angiography, Knowledge Based Segmentation, Probabilistic Atlas, Thin-Plate Spline, Distance Fields, Histogram Classification
Download full paper
Matúš Straka, Alexandra La Cruz, Leonid I. Dimitrov, Miloš Šrámek, Dominik Fleischmann, Eduard Gröller. "Bone Segmentation in CT-Angiography Data Using a Probabilistic Atlas"In proceedings of VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2003 (VMV2003), Full paper (729 KB)
BibTeX Entry
@InProceedings{Straka03BSA,
author = "Matúš Straka and Alexandra La Cruz and
Leonid I. Dimitrov and Miloš Šrámek and Dominik Fleischmann and
Eduard Gröller",
title = "Bone Segmentation in CT-Angiography Data Using
a Probabilistic Atlas",
bookTitle = "Proceedings of Vision Modeling and Visualization",
year = "2003",
pages = "505--512"
}