Information
- Publication Type: Bachelor Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: January 2023
- Date (Start): 23. April 2022
- Date (End): 28. January 2023
- Matrikelnummer: 01527619
- First Supervisor: Eduard Gröller
Abstract
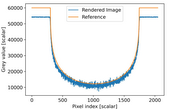
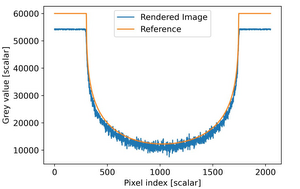
Computed tomography (CT) has a wide range of applications. It is an important technique in industrial non-destructive testing, where engineers want to find flaws in materials or reverse engineer the material composition of an object. Another application in material science is to visualize stresses that occur inside of an object. Furthermore, it is also often used in medical applications, however, the focus of this thesis lies on industrial computed tomography. Actual computed tomography scans can take quite a long time and may become expensive. Therefore, it is essential to create software simulations that allow fast and accurate prototyping of such scans, in order to keep cost and time consumption to a minimum. In this thesis, we present a method to create such scans using Monte Carlo based rendering methods and compare it to an existing solution regarding accuracy and time.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@bachelorsthesis{Philipp_Hochhauser_2023,
title = "X-ray Path Tracing for CT Imaging",
author = "Philipp Hochhauser",
year = "2023",
abstract = "Computed tomography (CT) has a wide range of applications.
It is an important technique in industrial non-destructive
testing, where engineers want to find flaws in materials or
reverse engineer the material composition of an object.
Another application in material science is to visualize
stresses that occur inside of an object. Furthermore, it is
also often used in medical applications, however, the focus
of this thesis lies on industrial computed tomography.
Actual computed tomography scans can take quite a long time
and may become expensive. Therefore, it is essential to
create software simulations that allow fast and accurate
prototyping of such scans, in order to keep cost and time
consumption to a minimum. In this thesis, we present a
method to create such scans using Monte Carlo based
rendering methods and compare it to an existing solution
regarding accuracy and time. ",
month = jan,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Research Unit of Computer Graphics, Institute of Visual
Computing and Human-Centered Technology, Faculty of
Informatics, TU Wien ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2023/Philipp_Hochhauser_2023/",
}
 BA_thesis
BA_thesis image
image