Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: May 2022
- Date (Start): 3. February 2021
- Date (End): 17. May 2022
- TU Wien Library:
- Diploma Examination: 27. June 2022
- Open Access: yes
- First Supervisor: Eduard Gröller
- Pages: 126
- Keywords: Multi-Modal Segmentation, Registration
Abstract
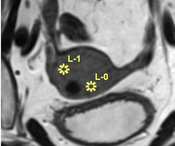
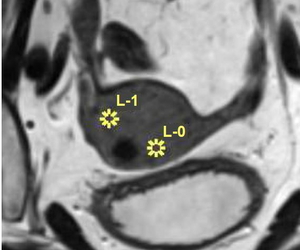
Endometrial cancer is the most common and most lethal gynecologic malignancy world-wide. Multiple MRI sequences are acquired per patient in gynecologic cancer research because they reveal different tissue characteristics. Radiomic tumor profiling extracts features from medical imaging data aiming to find new tumor imaging biomarkers. Co-registration and tumor segmentation of multi-sequential MRI data build the base for radiomic tumor profiling. Many approaches exist that aim to automate these time-consuming manual processes. After automatic co-registration, volumes are often still misaligned. This lack of registration quality has an impact on the results of radiomic tumor profiling, since we cannot ensure voxel integrity. We distinguish between rigid and deformable registration. Rigid registration transforms a volume using only translation and rotation parameters, while deformable registration can include local deformations. Tumors are rigid structures compared to the tissue around them. Therefore, rigid co-registration can be sufficient to align tumors. However, to analyze also surrounding structures, deformable registration is necessary. Even though tumors are rigid structures, they can appear slightly different in the varying sequences due to imaging physics. Applying deformable registration to the whole image can result in tumor deformations that do not resemble the underlying biological tissue characteristics and can alter important information about tumor tissue characteristics. To address these two problems, we propose the web-based application MuSIC (Multi-Sequential Interactive Co-registration). The tool allows medical experts to co-register multiple sequences simultaneously based on a pre-defined segmentation mask that has been generated for one of the sequences. In our workflow, a simulated-annealing-based shape matching algorithm searches for the tumor position in each sequence that can vary in translation and rotation parameters. We present the updated segmentation positions to the user, who can interactively adapt the positions if needed. We include multi-modal visualization techniques for visual quality assessment during this procedure. Based on the positioning of the segmentation masks, we register the volumes. We allow for both rigid and deformable co-registration. Due to our approach based on segmentation masks, we apply local transformations mainly outside the tumor tissue in deformable registration. We evaluate our approach in a usability analysis with medical and machine learning experts. They find the tool very intuitive and especially the medical experts clearly see themselves using MuSIC in the future.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
BibTeX
@mastersthesis{Eichner2022,
title = "Interactive Co-Registration for Multi-Modal Cancer Imaging
Data based on Segmentation Masks",
author = "Tanja Eichner",
year = "2022",
abstract = "Endometrial cancer is the most common and most lethal
gynecologic malignancy world-wide. Multiple MRI sequences
are acquired per patient in gynecologic cancer research
because they reveal different tissue characteristics.
Radiomic tumor profiling extracts features from medical
imaging data aiming to find new tumor imaging biomarkers.
Co-registration and tumor segmentation of multi-sequential
MRI data build the base for radiomic tumor profiling. Many
approaches exist that aim to automate these time-consuming
manual processes. After automatic co-registration, volumes
are often still misaligned. This lack of registration
quality has an impact on the results of radiomic tumor
profiling, since we cannot ensure voxel integrity. We
distinguish between rigid and deformable registration. Rigid
registration transforms a volume using only translation and
rotation parameters, while deformable registration can
include local deformations. Tumors are rigid structures
compared to the tissue around them. Therefore, rigid
co-registration can be sufficient to align tumors. However,
to analyze also surrounding structures, deformable
registration is necessary. Even though tumors are rigid
structures, they can appear slightly different in the
varying sequences due to imaging physics. Applying
deformable registration to the whole image can result in
tumor deformations that do not resemble the underlying
biological tissue characteristics and can alter important
information about tumor tissue characteristics. To address
these two problems, we propose the web-based application
MuSIC (Multi-Sequential Interactive Co-registration). The
tool allows medical experts to co-register multiple
sequences simultaneously based on a pre-defined
segmentation mask that has been generated for one of the
sequences. In our workflow, a simulated-annealing-based
shape matching algorithm searches for the tumor position in
each sequence that can vary in translation and rotation
parameters. We present the updated segmentation positions to
the user, who can interactively adapt the positions if
needed. We include multi-modal visualization techniques for
visual quality assessment during this procedure. Based on
the positioning of the segmentation masks, we register the
volumes. We allow for both rigid and deformable
co-registration. Due to our approach based on segmentation
masks, we apply local transformations mainly outside the
tumor tissue in deformable registration. We evaluate our
approach in a usability analysis with medical and machine
learning experts. They find the tool very intuitive and
especially the medical experts clearly see themselves using
MuSIC in the future.",
month = may,
pages = "126",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Research Unit of Computer Graphics, Institute of Visual
Computing and Human-Centered Technology, Faculty of
Informatics, TU Wien",
keywords = "Multi-Modal Segmentation, Registration",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2022/Eichner2022/",
}
 Image
Image Master Thesis
Master Thesis Poster
Poster