Information
- Publication Type: Conference Paper
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: October 2021
- Publisher: IEEE Computer Society Press
- Open Access: yes
- Lecturer: Manuela Waldner
- Event: IEEE Visualization Conference (VIS)
- DOI: 10.1109/VIS49827.2021.9623326
- Call for Papers: Call for Paper
- Booktitle: IEEE Visualization Conference (VIS)
- Pages: 5
- Pages: 61 – 65
Abstract
In visual interactive labeling, users iteratively assign labels to data items until the machine model reaches an acceptable accuracy. A crucial step of this process is to inspect the model's accuracy and decide whether it is necessary to label additional elements. In scenarios with no or very little labeled data, visual inspection of the predictions is required. Similarity-preserving scatterplots created through a dimensionality reduction algorithm are a common visualization that is used in these cases. Previous studies investigated the effects of layout and image complexity on tasks like labeling. However, model evaluation has not been studied systematically. We present the results of an experiment studying the influence of image complexity and visual grouping of images on model accuracy estimation. We found that users outperform traditional automated approaches when estimating a model's accuracy. Furthermore, while the complexity of images impacts the overall performance, the layout of the items in the plot has little to no effect on estimations.Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
 presentation:
Pre-recorded presentation for VIS 2021
presentation:
Pre-recorded presentation for VIS 2021
 preview:
Fast-forward preview video
preview:
Fast-forward preview video
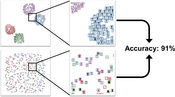 teaser:
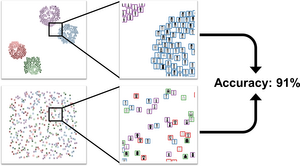
In both scatterplots shown here, the percentage of images with correctly predicted class labels (visualized as border color) is over 90%. We found that users can estimate these accuracies fairly well. Image complexity impacts overall performance, but the layout has very little effect on users’ estimations.
teaser:
In both scatterplots shown here, the percentage of images with correctly predicted class labels (visualized as border color) is over 90%. We found that users can estimate these accuracies fairly well. Image complexity impacts overall performance, but the layout has very little effect on users’ estimations.
Additional files
 supplement:
Supplementary document showing study conditions and interface
supplement:
Supplementary document showing study conditions and interface
Weblinks
- arxiv
Link to arxiv version of the paper - Entry in reposiTUm (TU Wien Publication Database)
- DOI: 10.1109/VIS49827.2021.9623326
BibTeX
@inproceedings{grossmann-2021-layout,
title = "Does the Layout Really Matter? A Study on Visual Model
Accuracy Estimation",
author = "Nicolas Grossmann and J\"{u}rgen Bernard and Michael
Sedlmair and Manuela Waldner",
year = "2021",
abstract = "In visual interactive labeling, users iteratively assign
labels to data items until the machine model reaches an
acceptable accuracy. A crucial step of this process is to
inspect the model's accuracy and decide whether it is
necessary to label additional elements. In scenarios with no
or very little labeled data, visual inspection of the
predictions is required. Similarity-preserving scatterplots
created through a dimensionality reduction algorithm are a
common visualization that is used in these cases. Previous
studies investigated the effects of layout and image
complexity on tasks like labeling. However, model evaluation
has not been studied systematically. We present the results
of an experiment studying the influence of image complexity
and visual grouping of images on model accuracy estimation.
We found that users outperform traditional automated
approaches when estimating a model's accuracy. Furthermore,
while the complexity of images impacts the overall
performance, the layout of the items in the plot has little
to no effect on estimations.",
month = oct,
publisher = "IEEE Computer Society Press",
event = "IEEE Visualization Conference (VIS)",
doi = "10.1109/VIS49827.2021.9623326",
booktitle = "IEEE Visualization Conference (VIS)",
pages = "5",
pages = "61--65",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2021/grossmann-2021-layout/",
}

 paper
paper