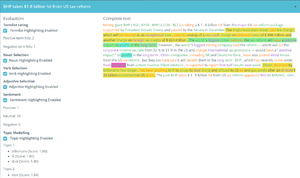
Information
- Publication Type: Bachelor Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: April 2018
- Date (Start): May 2017
- Date (End): April 2018
- Matrikelnummer: 01426853
- First Supervisor: Manuela Waldner
Abstract
Having to read and understand lots of text documents and reports on a daily basis can be quite challenging. The intended audience for these reports has limited resources and wants to reduce time spent on reading such reports. Therefore a need for a tool emerges that assists the process of gaining relevant information out of reports/documents more quickly. These text documents are often unstructured and of varying length. They are written in the English language and are available from different sources (such as RSS feeds and text files). The aim of this project is to offer a tool that supports the process of analysing and understanding given texts. This is made possible by using natural language processing (NLP) and text visualization (TextVis). TextVis is already a well known and frequently used solution. The herein described project uses an NLP pipeline which serves as preprocessing for TextVis. To provide quick insight into the data, topic extraction mechanisms like Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) or Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) are available for the user to be chosen within the aforementioned pipeline. A major challenge for TextVis is the configuration of the NLP pipeline, because there are many different ways of doing so and a wide range of parameters to chose from. To overcome this issue, this project provides a solution that enables users to easily configure and customize their own NLP pipeline. It is designed to encourage these users to experiment with different sequences of NLP operations and parameter configurations to find a solution that suites them best. In order to keep it easy to use the software, it is implemented entirely using web technologies to be accessible in a common web browser. The resulting visualization will emphasize particular parts of the text based on a set of different factors, if selected so. These factors can be topics, sentiments and part-of-speech-tagged words. The focus of this work lies on a visual interface that enables and encourages users to adjust/optimize the underlying NLP pipeline (by selecting steps and setting parameters) and comparing their results. Evaluation with help of user feedback showed that certain pipeline configurations work better for certain types of texts than others. Using the solution created within this work, users can adapt the tool to their needs and also tweak it according to requirements. There is no universal configuration that works for all documents, however.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@bachelorsthesis{smiech-2018-tei,
title = "Configurable Text Exploration Interface with NLP for
Decision Support",
author = "Martin Smiech",
year = "2018",
abstract = "Having to read and understand lots of text documents and
reports on a daily basis can be quite challenging. The
intended audience for these reports has limited resources
and wants to reduce time spent on reading such reports.
Therefore a need for a tool emerges that assists the process
of gaining relevant information out of reports/documents
more quickly. These text documents are often unstructured
and of varying length. They are written in the English
language and are available from different sources (such as
RSS feeds and text files). The aim of this project is to
offer a tool that supports the process of analysing and
understanding given texts. This is made possible by using
natural language processing (NLP) and text visualization
(TextVis). TextVis is already a well known and frequently
used solution. The herein described project uses an NLP
pipeline which serves as preprocessing for TextVis. To
provide quick insight into the data, topic extraction
mechanisms like Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) or
Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) are available for
the user to be chosen within the aforementioned pipeline. A
major challenge for TextVis is the configuration of the NLP
pipeline, because there are many different ways of doing so
and a wide range of parameters to chose from. To overcome
this issue, this project provides a solution that enables
users to easily configure and customize their own NLP
pipeline. It is designed to encourage these users to
experiment with different sequences of NLP operations and
parameter configurations to find a solution that suites them
best. In order to keep it easy to use the software, it is
implemented entirely using web technologies to be accessible
in a common web browser. The resulting visualization will
emphasize particular parts of the text based on a set of
different factors, if selected so. These factors can be
topics, sentiments and part-of-speech-tagged words. The
focus of this work lies on a visual interface that enables
and encourages users to adjust/optimize the underlying NLP
pipeline (by selecting steps and setting parameters) and
comparing their results. Evaluation with help of user
feedback showed that certain pipeline configurations work
better for certain types of texts than others. Using the
solution created within this work, users can adapt the tool
to their needs and also tweak it according to requirements.
There is no universal configuration that works for all
documents, however.",
month = apr,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2018/smiech-2018-tei/",
}