Information
- Publication Type: Bachelor Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: July 2018
- Date (Start): 8. March 2018
- Date (End): 8. July 2018
- Matrikelnummer: 01427382
- First Supervisor: Eduard Gröller
Abstract
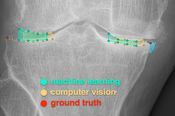
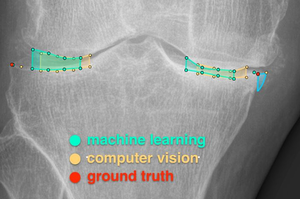
As artificial intelligence (AI) progresses with seemingly unstoppable speed, its wide field of applications broadens by the day. One area where AI advancements appear to be especially promising is their employment in the medical sector. Nowadays, due to the wider availability of processing power, algorithms based on neuronal networks can be used to generate far more data in areas where it previously seemed unthinkable. Traditional image-processing-algorithms often utilize computer vision (CV)-algorithms such as edge-detection to generate data from pixel input. While this method of gaining data worked well in the past, AI can help to improve the precision of such an analysis. The area I focussed on in this thesis is the generation of data from x-ray images of the knee joint. ImageBiopsy Lab (IB Lab)’s algorithms relied heavily on CV-based analysis for the diagnosis of osteoarthritis (OA) in the knee. While this yielded good results in the past, this work will show that the use of deep neuronal networks improves accuracy in a significant way. Further, neuronal networks can provide additional information that was a lot harder to be gained before, such as the laterality of a given image. The aim of this project was to diagnose OA faster and more precisely than in the past and to embed it into a web-based solution for broader accessibility. To showcase the benefits of the described method, at the time of writing, our software is in the stage of being rolled out in a hospital in Lower Austria. Because of the advancements mentioned above, this work will focus on the description and comparison of gaining information from x-ray images for a meaningful and efficient diagnosis of OA in the knee.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@bachelorsthesis{Masopust_2018,
title = "Web-Based Osteoarthritis-Analysis Generating Data from
Native Libraries and Machine-Learning Models",
author = "Lukas Masopust",
year = "2018",
abstract = "As artificial intelligence (AI) progresses with seemingly
unstoppable speed, its wide field of applications broadens
by the day. One area where AI advancements appear to be
especially promising is their employment in the medical
sector. Nowadays, due to the wider availability of
processing power, algorithms based on neuronal networks can
be used to generate far more data in areas where it
previously seemed unthinkable. Traditional
image-processing-algorithms often utilize computer vision
(CV)-algorithms such as edge-detection to generate data from
pixel input. While this method of gaining data worked well
in the past, AI can help to improve the precision of such an
analysis. The area I focussed on in this thesis is the
generation of data from x-ray images of the knee joint.
ImageBiopsy Lab (IB Lab)’s algorithms relied heavily on
CV-based analysis for the diagnosis of osteoarthritis (OA)
in the knee. While this yielded good results in the past,
this work will show that the use of deep neuronal networks
improves accuracy in a significant way. Further, neuronal
networks can provide additional information that was a lot
harder to be gained before, such as the laterality of a
given image. The aim of this project was to diagnose OA
faster and more precisely than in the past and to embed it
into a web-based solution for broader accessibility. To
showcase the benefits of the described method, at the time
of writing, our software is in the stage of being rolled out
in a hospital in Lower Austria. Because of the advancements
mentioned above, this work will focus on the description and
comparison of gaining information from x-ray images for a
meaningful and efficient diagnosis of OA in the knee. ",
month = jul,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2018/Masopust_2018/",
}
 image
image