Information
- Publication Type: Master Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: June 2014
- Date (Start): 28. June 2014
- Date (End): 28. June 2014
- TU Wien Library:
- First Supervisor: Eduard Gröller

Abstract
In the so called information age, data is widely available. Sources include data collection as a byproduct (e.g., log files on a server, or as a more concrete example, movement profiles of smartphone users) and data generation for particular purposes (e.g., simulation runs, data gathered from sensors). To benefit from
this huge amount of available data, the data must be analyzed and relevant information must be extracted.
Visual Analytics has become an important approach to identify and extract relevant information from data, especially with big data sets.
However, data can also contain erroneous values for different reasons, e.g., caused by defect sensors. In data warehousing projects, transforming and edit the data into a usable state can account up for 80% of the cost and the development time.
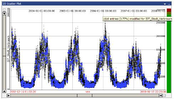
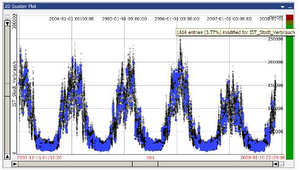
This diploma thesis focuses on time-dependent data and presents an extension for the existing visual
analytics framework VISPLORE, to support the user in the process of data editing. Using plausibility rules, the user can define data checks and imputation strategies. Three different overviews, a data-based overview, a group-based overview, and a rule-based overview provide insight into the structure of implausible data values and the defined plausibility rules. Implausible values can be imputed using the
defined imputation strategies and existing visualization techniques are extended to enable the user getting an overview of the modified values. Real-world data is used to demonstrate two use-cases. Limitations of the provided overviews, e.g., scalability for a large number of plausibility rules, are discussed and ideas
for future work are outlined.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
No further information available.
BibTeX
@mastersthesis{Moellinger_Christian_IDE2,
title = "Interactive Data Editing of Time-Dependent Data in Visual
Analysis",
author = "Christian M\"{o}llinger",
year = "2014",
abstract = "In the so called information age, data is widely available.
Sources include data collection as a byproduct (e.g., log
files on a server, or as a more concrete example, movement
profiles of smartphone users) and data generation for
particular purposes (e.g., simulation runs, data gathered
from sensors). To benefit from this huge amount of available
data, the data must be analyzed and relevant information
must be extracted. Visual Analytics has become an important
approach to identify and extract relevant information from
data, especially with big data sets. However, data can also
contain erroneous values for different reasons, e.g., caused
by defect sensors. In data warehousing projects,
transforming and edit the data into a usable state can
account up for 80% of the cost and the development time.
This diploma thesis focuses on time-dependent data and
presents an extension for the existing visual analytics
framework VISPLORE, to support the user in the process of
data editing. Using plausibility rules, the user can define
data checks and imputation strategies. Three different
overviews, a data-based overview, a group-based overview,
and a rule-based overview provide insight into the structure
of implausible data values and the defined plausibility
rules. Implausible values can be imputed using the defined
imputation strategies and existing visualization techniques
are extended to enable the user getting an overview of the
modified values. Real-world data is used to demonstrate two
use-cases. Limitations of the provided overviews, e.g.,
scalability for a large number of plausibility rules, are
discussed and ideas for future work are outlined. ",
month = jun,
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2014/Moellinger_Christian_IDE2/",
}
 master thesis
master thesis