Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: January 2016
- Journal: Visualization and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions on
- ISSN: 1077-2626
Abstract
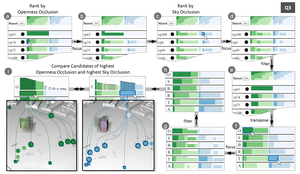
3D visibility analysis plays a key role in urban planning for assessing the visual impact of proposed buildings on the cityscape. A call for proposals typically yields around 30 candidate buildings that need to be evaluated with respect to selected viewpoints. Current visibility analysis methods are very time-consuming and limited to a small number of viewpoints. Further, analysts neither have measures to evaluate candidates quantitatively, nor to compare them efficiently. The primary contribution of this work is the design study of Vis-A-Ware, a visualization system to qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate, rank, and compare visibility data of candidate buildings with respect to a large number of viewpoints. Vis-A-Ware features a 3D spatial view of an urban scene and non-spatial views of data derived from visibility evaluations, which are tightly integrated by linked interaction. To enable a quantitative evaluation we developed four metrics in accordance with experts from urban planning. We illustrate the applicability of Vis-A-Ware on the basis of a use case scenario and present results from informal feedback sessions with domain experts from urban planning and development. This feedback suggests that Vis-A-Ware is a valuable tool for visibility analysis allowing analysts to answer complex questions more efficiently and objectively.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{ortner-2016-visaware,
title = "Vis-a-ware: Integrating spatial and non-spatial
visualization for visibility-aware urban planning",
author = "Thomas Ortner and Johannes Sorger and Harald Steinlechner
and Gerd Hesina and Harald Piringer and Eduard Gr\"{o}ller",
year = "2016",
abstract = "3D visibility analysis plays a key role in urban planning
for assessing the visual impact of proposed buildings on the
cityscape. A call for proposals typically yields around 30
candidate buildings that need to be evaluated with respect
to selected viewpoints. Current visibility analysis methods
are very time-consuming and limited to a small number of
viewpoints. Further, analysts neither have measures to
evaluate candidates quantitatively, nor to compare them
efficiently. The primary contribution of this work is the
design study of Vis-A-Ware, a visualization system to
qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate, rank, and compare
visibility data of candidate buildings with respect to a
large number of viewpoints. Vis-A-Ware features a 3D spatial
view of an urban scene and non-spatial views of data derived
from visibility evaluations, which are tightly integrated by
linked interaction. To enable a quantitative evaluation we
developed four metrics in accordance with experts from urban
planning. We illustrate the applicability of Vis-A-Ware on
the basis of a use case scenario and present results from
informal feedback sessions with domain experts from urban
planning and development. This feedback suggests that
Vis-A-Ware is a valuable tool for visibility analysis
allowing analysts to answer complex questions more
efficiently and objectively.",
month = jan,
journal = "Visualization and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions on",
issn = "1077-2626 ",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2016/ortner-2016-visaware/",
}