Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper with Conference Talk
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: September 2016
- Journal: Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and Medicine
- Lecturer:
- Pages: 193 – 202
Abstract
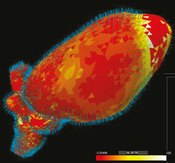
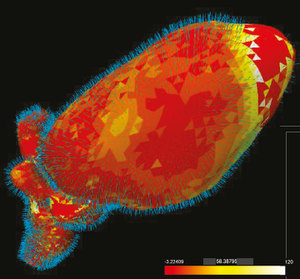
Several diagnostic and treatment procedures require the segmentation of anatomical structures from medical images. However, the automatic model-based methods that are often employed, may produce inaccurate segmentations. These, if used as input for diagnosis or treatment, can have detrimental effects for the patients. Currently, an analysis to predict which anatomic regions are more prone to inaccuracies, and to determine how to improve segmentation algorithms, cannot be performed. We propose a visual tool to enable experts, working on model-based segmentation algorithms, to explore and analyze the outcomes and errors of their methods. Our approach supports the exploration of errors in a cohort of pelvic organ segmentations, where the performance of an algorithm can be assessed. Also, it enables the detailed exploration and assessment of segmentation errors, in individual subjects. To the best of our knowledge, there is no other tool with comparable functionality. A usage scenario is employed to explore and illustrate the capabilities of our visual tool. To further assess the value of the proposed tool, we performed an evaluation with five segmentation experts. The evaluation participants confirmed the potential of the tool in providing new insight into their data and employed algorithms. They also gave feedback for future improvements.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@article{Groeller_2016_P4,
title = "Visual Analytics for the Exploration and Assessment of
Segmentation Errors",
author = "Renata Raidou and Freek Marcelis and Marcel Breeuwer and
Eduard Gr\"{o}ller and Anna Vilanova i Bartroli and Huub van
de Wetering",
year = "2016",
abstract = "Several diagnostic and treatment procedures require the
segmentation of anatomical structures from medical images.
However, the automatic model-based methods that are often
employed, may produce inaccurate segmentations. These, if
used as input for diagnosis or treatment, can have
detrimental effects for the patients. Currently, an analysis
to predict which anatomic regions are more prone to
inaccuracies, and to determine how to improve segmentation
algorithms, cannot be performed. We propose a visual tool to
enable experts, working on model-based segmentation
algorithms, to explore and analyze the outcomes and errors
of their methods. Our approach supports the exploration of
errors in a cohort of pelvic organ segmentations, where the
performance of an algorithm can be assessed. Also, it
enables the detailed exploration and assessment of
segmentation errors, in individual subjects. To the best of
our knowledge, there is no other tool with comparable
functionality. A usage scenario is employed to explore and
illustrate the capabilities of our visual tool. To further
assess the value of the proposed tool, we performed an
evaluation with five segmentation experts. The evaluation
participants confirmed the potential of the tool in
providing new insight into their data and employed
algorithms. They also gave feedback for future improvements.",
month = sep,
journal = "Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and
Medicine",
pages = "193--202",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2016/Groeller_2016_P4/",
}

 image
image Paper
Paper