Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper (without talk)
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: January 2011
- ISSN: 0010-4485
- Journal: Computer-Aided Design
- Number: 1
- Volume: 43
- Pages: 1629 – 1638
- Keywords: EMST, Curve, Point cloud, Reconstruction, Shape Construction, Boundary, Computational geometry, Point set
Abstract
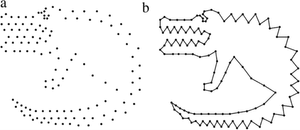
Given an unorganized two-dimensional point cloud, we address the problem of efficiently constructing a single aesthetically pleasing closed interpolating shape, without requiring dense or uniform spacing. Using Gestalt’s laws of proximity, closure and good continuity as guidance for visual aesthetics, we require that our constructed shape be a minimal perimeter, non-self intersecting manifold. We find that this yields visually pleasing results. Our algorithm is distinct from earlier shape reconstruction approaches, in that it exploits the overlap between the desired shape and a related minimal graph, the Euclidean Minimum Spanning Tree (EMST). Our algorithm segments the EMST to retain as much of it as required and then locally partitions and solves the problem efficiently. Comparison with some of the best currently known solutions shows that our algorithm yields better results.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
BibTeX
@article{ohrhallinger_stefan-2011-001,
title = "Interpolating an unorganized 2D point cloud with a single
closed shape",
author = "Stefan Ohrhallinger and Sudhir Mudur",
year = "2011",
abstract = "Given an unorganized two-dimensional point cloud, we address
the problem of efficiently constructing a single
aesthetically pleasing closed interpolating shape, without
requiring dense or uniform spacing. Using Gestalt’s laws
of proximity, closure and good continuity as guidance for
visual aesthetics, we require that our constructed shape be
a minimal perimeter, non-self intersecting manifold. We find
that this yields visually pleasing results. Our algorithm is
distinct from earlier shape reconstruction approaches, in
that it exploits the overlap between the desired shape and a
related minimal graph, the Euclidean Minimum Spanning Tree
(EMST). Our algorithm segments the EMST to retain as much of
it as required and then locally partitions and solves the
problem efficiently. Comparison with some of the best
currently known solutions shows that our algorithm yields
better results. ",
month = jan,
issn = "0010-4485",
journal = "Computer-Aided Design",
number = "1",
volume = "43",
pages = "1629--1638",
keywords = "EMST, Curve, Point cloud, Reconstruction, Shape
Construction, Boundary, Computational geometry, Point set",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2011/ohrhallinger_stefan-2011-001/",
}

 paper
paper