Information
- Publication Type: PhD-Thesis
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: December 2009
- Date (Start): December 2005
- Date (End): December 2009
- TU Wien Library:
- Open Access: yes
- 2nd Reviewer: Ivan Viola
- Rigorosum: 11. December 2009
- First Supervisor: Eduard Gröller
- Pages: 105
- Keywords: marching cubes, feature peeling, difference measurement, multiple datasets, parameter visualization, comparative visualization, industrial computed tomography, volume visualization, fabrication artifacts, magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
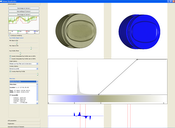
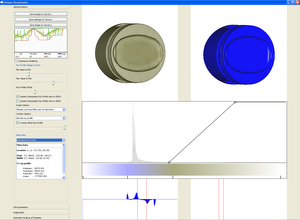
This thesis presents techniques and algorithms for the effective exploration of volumetric datasets. The Visualization techniques are designed to focus on user specified features of interest. The proposed techniques are grouped into four chapters namely feature peeling, computation and visualization of fabrication artifacts, locally adaptive marching cubes, and comparative visualization for parameter studies of dataset series. The presented methods enable the user to efficiently explore the volumetric dataset for features of interest.Feature peeling is a novel rendering algorithm that analyzes ray profiles along lines of sight. The profiles are subdivided according to encountered peaks and valleys at so called transition points. The sensitivity of these transition points is calibrated via two thresholds. The slope threshold is based on the magnitude of a peak following a valley, while the peeling threshold measures the depth of the transition point relative to the neighboring rays. This technique separates the dataset into a number of feature layers.
Fabrication artifacts are of prime importance for quality control engineers for first part inspection of industrial components. Techniques are presented in this thesis to measure fabrication artifacts through direct comparison of a reference CAD model with the corresponding industrial 3D X-ray computed tomography volume. Information from the CAD model is used to locate corresponding points in the volume data. Then various comparison metrics are computed to measure differences (fabrication artifacts) between the CAD model and the volumetric dataset. The comparison metrics are classified as either geometry-driven comparison techniques or visual-driven comparison techniques.
The locally adaptive marching cubes algorithm is a modification of the marching cubes algorithm where instead of a global iso-value, each grid point has its own iso-value. This defines an iso-value field, which modifies the case identification process in the algorithm. An iso-value field enables the algorithm to correct biases within the dataset like low frequency noise, contrast drifts, local density variations, and other artifacts introduced by the measurement process. It can also be used for blending between different iso-surfaces (e.g., skin, and bone in a medical dataset).
Comparative visualization techniques are proposed to carry out parameter studies for the special application area of dimensional measurement using industrial 3D X-ray computed tomography. A dataset series is generated by scanning a specimen multiple times by varying parameters of the scanning device. A high resolution series is explored using a planar reformatting based visualization system. A multi-image view and an edge explorer are proposed for comparing and visualizing gray values and edges of several datasets simultaneously. For fast data retrieval and convenient usability the datasets are bricked and efficient data structures are used.
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
BibTeX
@phdthesis{malik-thesis,
title = "Feature Centric Volume Visualization",
author = "Muhammad Muddassir Malik",
year = "2009",
abstract = "This thesis presents techniques and algorithms for the
effective exploration of volumetric datasets. The
Visualization techniques are designed to focus on user
specified features of interest. The proposed techniques are
grouped into four chapters namely feature peeling,
computation and visualization of fabrication artifacts,
locally adaptive marching cubes, and comparative
visualization for parameter studies of dataset series. The
presented methods enable the user to efficiently explore the
volumetric dataset for features of interest. Feature
peeling is a novel rendering algorithm that analyzes ray
profiles along lines of sight. The profiles are subdivided
according to encountered peaks and valleys at so called
transition points. The sensitivity of these transition
points is calibrated via two thresholds. The slope threshold
is based on the magnitude of a peak following a valley,
while the peeling threshold measures the depth of the
transition point relative to the neighboring rays. This
technique separates the dataset into a number of feature
layers. Fabrication artifacts are of prime importance for
quality control engineers for first part inspection of
industrial components. Techniques are presented in this
thesis to measure fabrication artifacts through direct
comparison of a reference CAD model with the corresponding
industrial 3D X-ray computed tomography volume. Information
from the CAD model is used to locate corresponding points in
the volume data. Then various comparison metrics are
computed to measure differences (fabrication artifacts)
between the CAD model and the volumetric dataset. The
comparison metrics are classified as either geometry-driven
comparison techniques or visual-driven comparison
techniques. The locally adaptive marching cubes algorithm
is a modification of the marching cubes algorithm where
instead of a global iso-value, each grid point has its own
iso-value. This defines an iso-value field, which modifies
the case identification process in the algorithm. An
iso-value field enables the algorithm to correct biases
within the dataset like low frequency noise, contrast
drifts, local density variations, and other artifacts
introduced by the measurement process. It can also be used
for blending between different iso-surfaces (e.g., skin, and
bone in a medical dataset). Comparative visualization
techniques are proposed to carry out parameter studies for
the special application area of dimensional measurement
using industrial 3D X-ray computed tomography. A dataset
series is generated by scanning a specimen multiple times by
varying parameters of the scanning device. A high resolution
series is explored using a planar reformatting based
visualization system. A multi-image view and an edge
explorer are proposed for comparing and visualizing gray
values and edges of several datasets simultaneously. For
fast data retrieval and convenient usability the datasets
are bricked and efficient data structures are used.",
month = dec,
pages = "105",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
school = "Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna
University of Technology ",
keywords = "marching cubes, feature peeling, difference measurement,
multiple datasets, parameter visualization, comparative
visualization, industrial computed tomography, volume
visualization, fabrication artifacts, magnetic resonance
imaging",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2009/malik-thesis/",
}

 Thesis
Thesis