Information
- Publication Type: Journal Paper (without talk)
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: May 2012
- Journal: Computers & Graphics
- Number: 3
- Volume: 36
- Pages: 201 – 213
- Keywords: shader augmentation, semantic visualization mapping, illustrative visualization, Volume rendering
Abstract
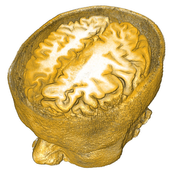
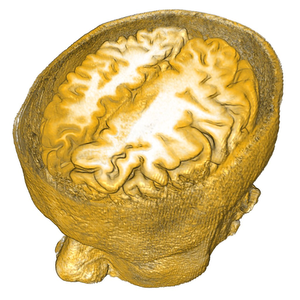
We present an interactive graphical approach for the explicit specification of semantics for volume visualization. This explicit and graphical specification of semantics for volumetric features allows us to visually assign meaning to both input and output parameters of the visualization mapping. This is in contrast to the implicit way of specifying semantics using transfer functions. In particular, we demonstrate how to realize a dynamic specification of semantics which allows to flexibly explore a wide range of mappings. Our approach is based on three concepts. First, we use semantic shader augmentation to automatically add rule-based rendering functionality to static visualization mappings in a shader program, while preserving the visual abstraction that the initial shader encodes. With this technique we extend recent developments that define a mapping between data attributes and visual attributes with rules, which are evaluated using fuzzy logic. Second, we let users define the semantics by analogy through brushing on renderings of the data attributes of interest. Third, the rules are specified graphically in an interface that provides visual clues for potential modifications. Together, the presented methods offer a high degree of freedom in the specification and exploration of rule-based mappings and avoid the limitations of a linguistic rule formulation.Additional Files and Images
Weblinks
No further information available.BibTeX
@article{Peter_2012_AIV,
title = "Semantics by Analogy for Illustrative Volume Visualization",
author = "Moritz Gerl and Peter Rautek and Tobias Isenberg and Eduard
Gr\"{o}ller",
year = "2012",
abstract = "We present an interactive graphical approach for the
explicit specification of semantics for volume
visualization. This explicit and graphical specification of
semantics for volumetric features allows us to visually
assign meaning to both input and output parameters of the
visualization mapping. This is in contrast to the implicit
way of specifying semantics using transfer functions. In
particular, we demonstrate how to realize a dynamic
specification of semantics which allows to flexibly explore
a wide range of mappings. Our approach is based on three
concepts. First, we use semantic shader augmentation to
automatically add rule-based rendering functionality to
static visualization mappings in a shader program, while
preserving the visual abstraction that the initial shader
encodes. With this technique we extend recent developments
that define a mapping between data attributes and visual
attributes with rules, which are evaluated using fuzzy
logic. Second, we let users define the semantics by analogy
through brushing on renderings of the data attributes of
interest. Third, the rules are specified graphically in an
interface that provides visual clues for potential
modifications. Together, the presented methods offer a high
degree of freedom in the specification and exploration of
rule-based mappings and avoid the limitations of a
linguistic rule formulation.",
month = may,
journal = "Computers & Graphics",
number = "3",
volume = "36",
pages = "201--213",
keywords = "shader augmentation, semantic visualization mapping,
illustrative visualization, Volume rendering",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2012/Peter_2012_AIV/",
}

 Paper
Paper