Information
- Replaced by: zsolnaifeher-2020-pme
- Publication Type: Technical Report
- Workgroup(s)/Project(s):
- Date: September 2019
- Number: TR-193-02-2019-3
- Open Access: yes
- Keywords: neural rendering, neural networks, photorealistic rendering, photorealistic material editing
Abstract
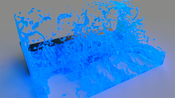
Creating photorealistic materials for light transport algorithms requires carefully fine-tuning a set of material properties to achieve a desired artistic effect. This is typically a lengthy process that involves a trained artist with specialized knowledge. In this work, we present a technique that aims to empower novice and intermediate-level users to synthesize high-quality photorealistic materials by only requiring basic image processing knowledge. In the proposed workflow, the user starts with an input image and applies a few intuitive transforms (e.g., colorization, image inpainting) within a 2D image editor of their choice, and in the next step, our technique produces a photorealistic result that approximates this target image. Our method combines the advantages of a neural network-augmented optimizer and an encoder neural network to produce high-quality output results within 30 seconds. We also demonstrate that it is resilient against poorly-edited target images and propose a simple extension to predict image sequences with a strict time budget of 1-2 seconds per image.Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8eNHEaxsj18
Additional Files and Images
Additional images and videos
Additional files
Weblinks
BibTeX
@techreport{zsolnaifeher-2019-pme,
title = "Photorealistic Material Editing Through Direct Image
Manipulation",
author = "Karoly Zsolnai-Feh\'{e}r and Peter Wonka and Michael Wimmer",
year = "2019",
abstract = "Creating photorealistic materials for light transport
algorithms requires carefully fine-tuning a set of material
properties to achieve a desired artistic effect. This is
typically a lengthy process that involves a trained artist
with specialized knowledge. In this work, we present a
technique that aims to empower novice and intermediate-level
users to synthesize high-quality photorealistic materials by
only requiring basic image processing knowledge. In the
proposed workflow, the user starts with an input image and
applies a few intuitive transforms (e.g., colorization,
image inpainting) within a 2D image editor of their choice,
and in the next step, our technique produces a
photorealistic result that approximates this target image.
Our method combines the advantages of a neural
network-augmented optimizer and an encoder neural network to
produce high-quality output results within 30 seconds. We
also demonstrate that it is resilient against poorly-edited
target images and propose a simple extension to predict
image sequences with a strict time budget of 1-2 seconds per
image. Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8eNHEaxsj18",
month = sep,
number = "TR-193-02-2019-3",
address = "Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria",
institution = "Research Unit of Computer Graphics, Institute of Visual
Computing and Human-Centered Technology, Faculty of
Informatics, TU Wien ",
note = "human contact: technical-report@cg.tuwien.ac.at",
keywords = "neural rendering, neural networks, photorealistic rendering,
photorealistic material editing",
URL = "https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2019/zsolnaifeher-2019-pme/",
}


 image
image paper
paper supplementary materials
supplementary materials