Speaker: Zhanyi Wu (University of Zürich)
Abstract
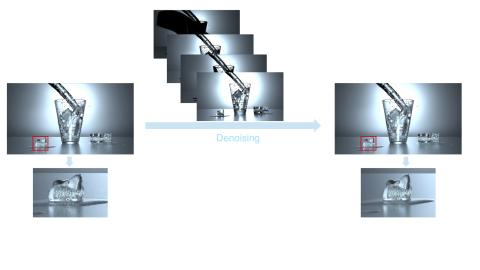
In this talk, we present a new noise-reduction technique for Monte Carlo rendering that builds on the intrinsic structure of sampled values rather than assuming any specific distribution or relying on pretraining. By analyzing how samples are arranged within their own distribution, the method extracts stable, distribution-aware features that remain reliable even in the presence of extreme outliers or heavy-tailed behaviors—patterns that frequently arise in physically based rendering.
Using this representation, we introduce an efficient correction mechanism that refines raw Monte Carlo estimates before aggregation. This approach naturally adapts to non-Gaussian sample statistics, enabling effective suppression of high-variance artifacts while retaining fine geometric and shading details. Because the method does not depend on neural networks or large auxiliary buffers, it integrates smoothly into existing pipelines and can run efficiently on modern GPU hardware.
Our results demonstrate clear advantages in mid-sample regimes, where traditional filters struggle with unstable noise patterns. The technique offers predictable convergence, low bias, and artifact-free reconstruction—providing a practical and robust alternative for high-quality MC denoising.